
BE THE FIRST TO KNOW
Enter your email below to subscribe to the QLA newsletter to receive timely updates from your favorites products.
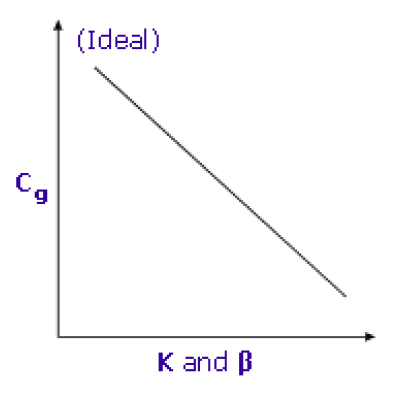
Lower K and β result in higher Cg and better sensitivity
Partition coefficients and phase ratios work together to determine the final concentration of volatile compounds in the headspace of sample vials.
The concentration of volatile compounds in the gas phase can be expressed as:
Cg = Co / (K + β)
where
Cg is the concentration of volatile analytes in the gas phase
and
Co is the original concentration of volatile analytes in the sample.
Striving for the lowest values for both K and β will result in higher concentrations of volatile analytes in the gas phase and therefore better sensitivity.